AI for Doctors: Changing Healthcare Today

Are you looking for a quick overview of how AI for doctors is changing medicine? Here's what you need to know:
- What it is: Artificial intelligence (AI) helps doctors with tasks that normally take a lot of time.
- How it's used: Doctors use AI for writing notes, summarizing research, and even helping with diagnoses.
- Key benefits: It greatly reduces paperwork and can make diagnoses more accurate.
- Main concerns: Doctors worry about patient privacy, how well AI fits into their existing tools, and who is responsible if AI makes a mistake.
The world of medicine is changing fast, and artificial intelligence (AI) is leading the way. Today, more and more doctors are using smart tools to help them every day. These tools are not just for the future; they are here now, making a real difference in clinics and hospitals.
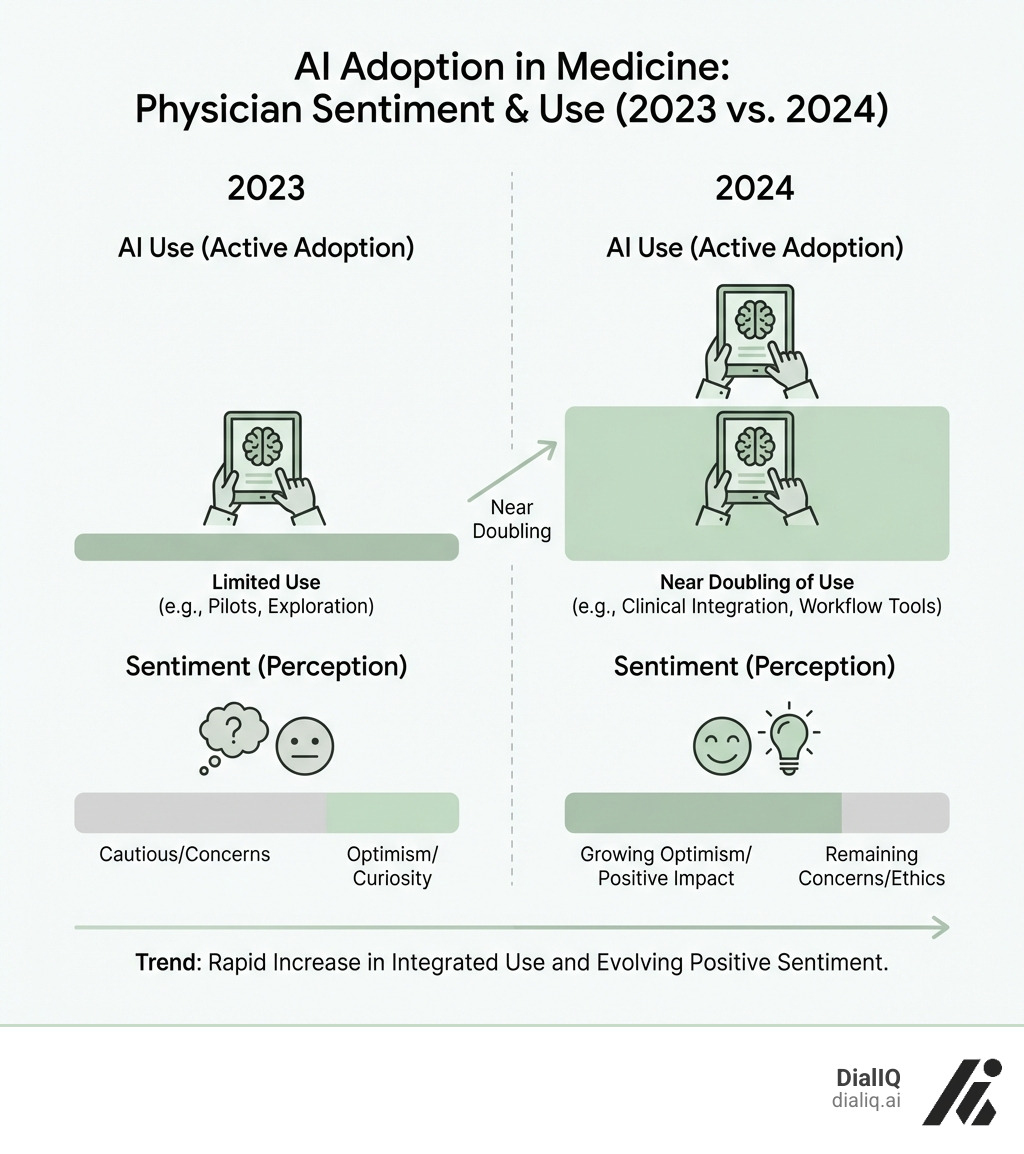
In fact, the number of doctors using AI has nearly doubled in just one year. This shows how quickly these technologies are becoming a key part of healthcare. Doctors are excited about the possibilities, especially how AI can cut down on the piles of paperwork they face daily. This frees them up to focus on what matters most: their patients.
But it's not all smooth sailing. While AI offers huge benefits, like helping with diagnoses and managing patient information, there are also important questions. Things like keeping patient data safe and making sure the AI works perfectly are big concerns for doctors. They want to make sure AI helps them do their jobs better, without adding new risks.
This guide will explore how AI is already reshaping medical practice, the specific tools doctors are using, and the challenges we need to address. It's about how AI can become a trusted partner, not a replacement, for doctors everywhere.
My name is Shaunak, and I'm building DialIQ, an AI receptionist designed to answer every business call 24/7. My experience creating industry-specific solutions for over 40 sectors, including medical, has given me deep insights into the practical applications of AI for doctors in streamlining operations.
How AI is Actively Reshaping Daily Medical Practice
The integration of artificial intelligence into healthcare is no longer a futuristic dream; it's a present-day reality actively changing how physicians approach their daily tasks. From the moment a patient's data enters the system to the final treatment plan, AI is proving to be an indispensable assistant.
This technological shift aims to improve diagnostic accuracy, significantly reduce the administrative load that often leads to physician burnout, and pave the way for highly personalized medicine. Let's dig into how AI is making these changes happen.
Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy and Patient Care
One of AI's most impactful applications is augmenting diagnostic processes. AI excels at analyzing vast amounts of data with speed and consistency. In radiology and pathology, algorithms scrutinize medical images like X-rays and MRIs to detect subtle anomalies the human eye might miss. Some AI systems have shown remarkable performance in detecting certain cancers and cardiac arrhythmias, acting as a specialized second pair of eyes for the clinician.
Beyond image analysis, large language models (LLMs) are proving competitive in diagnostic reasoning. Studies show LLMs can perform comparably to humans in simulated tests, helping to identify difficult cases. They can synthesize data from electronic health records (EHRs), create structured overviews, and suggest differential diagnoses with justifications.
However, limitations are significant. AI lacks direct patient interaction, cannot read non-verbal cues, and may struggle with novel cases outside its training data. The risk of misdiagnosis from AI "hallucinations" (confident but incorrect responses) underscores the critical need for human oversight in every step. The goal is to use AI to augment, not replace, a physician's expertise. You can explore a study on AI diagnostic reasoning here.
Streamlining Administrative Tasks to Reduce Burnout
Administrative burdens are a leading cause of physician burnout, and this is precisely where AI for doctors can deliver immediate benefits. A recent AMA survey found that 57% of physicians see reducing these tasks as AI's biggest opportunity. Adoption is growing: in 2024, 21% of physicians used AI for documentation (up from 13% in 2023), and 20% used it for creating care plans and progress notes.
Tools like AI scribes and ambient listening technology are game-changers. They allow a doctor to have a natural conversation with a patient while an AI transcribes and drafts clinical notes into the EHR. This lets physicians focus on the patient, not the computer.
Beyond notes, AI can automate other tedious tasks:
- Prior Authorization: Streamlining insurance approvals.
- Billing and Coding: Suggesting accurate codes to reduce errors.
- Patient Communication: Handling routine inquiries and reminders.
- Chart Summaries: Generating concise overviews of patient records.
Our own solutions, like DialIQ's AI receptionist, are purpose-built to handle patient calls, schedule appointments, and manage inquiries 24/7. This automation gives doctors back their time, reduces stress, and allows them to focus on practicing medicine. The AMA is actively exploring these applications to alleviate the administrative load. Read more about the AMA's perspective on AI in healthcare.
The Dawn of AI-Powered Personalized Treatment
The era of "one-size-fits-all" medicine is ending, thanks to AI for doctors. AI-powered personalized treatment is now achievable by processing complex biological and clinical data. Key areas include:
- Genomic Analysis: AI can analyze a patient's genetic makeup to identify disease predispositions and predict drug responses, allowing for highly targeted therapies.
- Predictive Analytics: By analyzing vast patient datasets, AI can forecast disease progression and identify high-risk patients, shifting healthcare from reactive to proactive.
- Evidence-Based Planning: AI tools can aggregate millions of de-identified health records, allowing doctors to query real-world evidence to inform treatment decisions for similar patient scenarios. This leads to more effective and safer regimens.
- Drug Findy: AI is dramatically accelerating drug findy and development by identifying drug candidates and predicting their efficacy, shortening timelines and reducing costs.
By integrating genomic insights, predictive models, and real-world evidence, AI empowers physicians to craft treatment plans that are more precise and truly personalized.
A Practical Guide to AI for Doctors: Tools and Applications
Understanding the theoretical benefits of AI is one thing, but seeing it in action with concrete tools makes it truly impactful. For doctors, the landscape of AI tools is rapidly expanding, offering practical solutions that fit into their daily workflows. These tools often leverage advanced technologies like Large Language Models (LLMs), generative AI, conversational AI, and sophisticated foundation models.

Let's explore some of the key applications and specific tools that are changing the game for healthcare professionals.
Leveraging LLMs like ChatGPT and Med-PaLM in a Medical Context
Large Language Models (LLMs) are at the forefront of generative AI, capable of understanding, generating, and summarizing human-like text. For AI for doctors, these models offer immense potential, acting as intelligent assistants that can process and synthesize vast amounts of medical information.
- ChatGPT Health: OpenAI, the creator of ChatGPT, launched ChatGPT Health to offer improved security for sharing medical records and data. While consumer-facing versions like the standard ChatGPT are widely used for wellness advice (hundreds of millions consult it weekly), specialized versions are being developed for clinical use. Physicians can use LLMs to query medical knowledge, summarize complex research papers, or draft patient-friendly explanations of diagnoses and treatments. Learn about OpenAI's announcement of ChatGPT Health.
- Med-PaLM: Google's Med-PaLM is a prominent example of an LLM specifically trained on medical data. These models are designed to excel in medical contexts, performing well on medical licensing exams and offering expert-level clinical knowledge. They can assist in generating differential diagnoses, providing evidence-based answers to clinical questions, and even drafting patient messages or educational materials.
While LLMs are powerful, it's crucial to remember their limitations. They can sometimes "hallucinate," providing confident but incorrect information, and consumer-grade LLMs are not regulated by health privacy laws like HIPAA. Therefore, human clinicians must always review and validate any information generated by these models, especially when it pertains to direct patient care. They are powerful tools for information retrieval and synthesis, but not substitutes for clinical judgment.
Specific AI Tools Changing the Physician's Workflow
Beyond general LLMs, a variety of purpose-built AI tools are specifically designed to integrate into a physician's daily workflow, making it more efficient and patient-centered.
- AI Scribes and Ambient Listening Technology: These tools are powerful in combating administrative burden. They use ambient listening to capture doctor-patient conversations in real-time, then automatically generate clinical notes, populate EHRs, and suggest billing codes. This allows doctors to focus on the patient instead of typing, freeing up significant time spent on charting after hours.
- Evidence Synthesis Tools: These platforms act like a specialized search engine for medical professionals, providing quick access to exhaustive medical knowledge. They aggregate content from leading medical journals and societies, allowing physicians to rapidly find up-to-date information for complex cases.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): These systems use AI to analyze patient data and provide alerts or recommendations at the point of care. They can help physicians adhere to best practices, identify potential drug interactions, or suggest diagnostic tests based on a patient's symptoms.
Here's a list of common tasks where physicians are most frequently using AI, based on recent surveys:
- Documentation: Generating billing codes, medical charts, and visit notes (used by 21% of physicians in 2024).
- Creation of Discharge Instructions/Care Plans: Drafting clear post-visit instructions and treatment plans (used by 20% of physicians).
- Translation Services: Facilitating communication with non-English speaking patients (used by 14% of physicians).
- Summarizing Medical Research and Standards of Care: Quickly distilling vast amounts of medical literature (used by 13% of physicians).
- Assistive Diagnosis: Offering diagnostic support and differential diagnoses (used by 12% of physicians).
- Generation of Chart Summaries: Creating concise overviews of patient histories (used by 12% of physicians).
- Patient-Facing Chatbots for Customer Service Functions: Handling routine patient inquiries (used by 10% of physicians).
- Patient-Facing Health Recommendations and Self-Care Engagement: Providing general health advice (used by 10% of physicians).
These tools are not just about making things faster; they're about making healthcare smarter, more efficient, and ultimately, more human, by allowing doctors to focus on the art of medicine rather than the science of administration.
Navigating the Challenges and Ethical Landscape of Medical AI
While the potential of AI for doctors is immense, its integration into healthcare comes with significant challenges and ethical considerations that we must address thoughtfully. Just as we wouldn't let a self-driving car hit the road without rigorous safety protocols, we must ensure medical AI operates within clear boundaries, prioritizing patient well-being above all else.
Key Concerns for Physicians: Trust, Privacy, and Accuracy
For AI to truly become a trusted co-pilot for doctors, several critical concerns need to be resolved:
- Data Security and Patient Privacy (HIPAA): Protecting sensitive health data is paramount. Physicians worry about data storage, third-party access, and the use of de-identified data. Patients must be informed if conversations are recorded and who reviews AI-generated notes.
- Risk of Misdiagnosis: AI is not infallible. "Hallucinations"—confident but fabricated information—pose a serious risk. A documented case of harmful AI advice highlights the danger of using AI without human oversight. You can read about a documented case of AI giving harmful advice.
- The "Black Box" Problem and Bias: Many AI models are "black boxes," making it hard to understand their reasoning. This lack of transparency is a barrier to trust. Furthermore, if training data is biased, the AI can perpetuate healthcare disparities, leading to unequal care.
- Liability and Accountability: Clear legal frameworks are needed to determine who is responsible if an AI error causes patient harm—the developer, the physician, or the hospital.
- Potential for Depersonalization: Over-reliance on AI for communication could depersonalize the patient experience, which requires empathy and human connection.
To build trust, physicians need robust data privacy, seamless workflow integration, and adequate training.
The Role of the AMA and Regulatory Bodies in AI for doctors
Professional organizations and regulatory bodies are guiding the responsible integration of AI. The American Medical Association (AMA) is a key voice, advocating for "augmented intelligence"—using AI to improve human capabilities, not replace them. The AMA's policies focus on patient education, protection from misleading AI advice, and establishing ethical guidelines.
Key principles include designing AI as an assistive tool, ensuring transparency, mitigating bias, and establishing clear legal frameworks for liability. Regulatory bodies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are also developing frameworks to ensure the safety and effectiveness of AI-enabled medical software. This oversight is critical, as 47% of physicians rank it as the top action needed to boost their trust in AI. The goal is a regulatory environment that fosters innovation while ensuring only safe, validated AI tools reach the market, protecting patients and building physician confidence. You can explore the AMA's comprehensive report on generative AI in medicine.
The Future Outlook: Your Practice with an AI Co-pilot
Looking ahead, the future of AI for doctors promises an even deeper integration into every facet of healthcare. We envision a future where AI acts as a constant "co-pilot," empowering physicians to deliver care that is more precise, efficient, and compassionate than ever before. This evolution will not only transform individual practices but also reshape the entire healthcare system and even medical education.
What's Next for AI for doctors?
The advancements we're seeing today are just the beginning. Here's a glimpse into what's next for AI in medicine:
- Agentic AI Teammates: Future AI systems will autonomously plan and execute tasks under a physician's supervision, such as managing chronic conditions based on real-time data or assisting in surgical planning.
- Automated Scientific Findy: The next frontier involves AI agents that can hypothesize new drugs, design and run experiments in robotic labs, and analyze results, dramatically accelerating medical breakthroughs.
- Conversational Diagnostic AI: Sophisticated conversational AI will engage in nuanced diagnostic dialogues with patients, gathering histories and suggesting diagnoses with high accuracy, assisting doctors in complex cases. Dive deeper into conversational diagnostic artificial intelligence.
- Predictive Health Modeling: AI will become more adept at predicting health trends by integrating data from EHRs, genomics, and wearables to enable proactive and preventive healthcare.
- Evolving Patient-Physician Relationship: With AI handling administrative tasks, doctors will have more time for empathy and communication. The relationship will become more collaborative, with physicians guiding better-informed patients.
- New Medical Education: Medical training will incorporate AI literacy, teaching future doctors how to collaborate with AI tools, evaluate their outputs, and understand the ethical implications.
The future is not about replacing doctors but augmenting their abilities with powerful cognitive assistants to achieve higher standards of care.
Frequently Asked Questions about AI in Medicine
We understand that the rapid evolution of AI in healthcare can raise many questions. Here, we address some of the most common inquiries about AI for doctors.
Will AI replace doctors?
This is perhaps the most common and understandable question. Our short answer is no, AI will not replace doctors. Our longer answer is that AI is designed to augment, not replace, human intelligence and expertise.
Think of AI as a sophisticated co-pilot or an invaluable tool in a doctor's toolkit, much like a stethoscope or an MRI machine. Its primary role is to improve physician capabilities, reduce administrative burdens, and provide data-driven insights. While AI can perform tasks like analyzing medical images, drafting notes, or suggesting diagnoses, the ultimate responsibility for patient care, complex decision-making, and empathetic interaction remains firmly with the human physician.
AI excels at data processing, pattern recognition, and automating repetitive tasks. Doctors excel at critical thinking, adapting to novel situations, understanding human nuances, and providing compassionate care. The future of medicine lies in a collaborative model where doctors leverage AI to be more efficient, accurate, and present for their patients, focusing on the human-centric skills that no machine can replicate.
What are the biggest risks of using AI in healthcare?
While the benefits are clear, we must also be clear-eyed about the potential risks associated with integrating AI into healthcare:
- Misdiagnosis and "Hallucinations": AI models can make errors, especially if trained on incomplete or biased data. The phenomenon of "hallucinations," where AI generates confident but factually incorrect information, poses a direct threat to patient safety if not carefully overseen by a human expert.
- Data Privacy Breaches: Healthcare data is highly sensitive. The vast amounts of patient information processed by AI systems increase the risk of data breaches and misuse, despite robust security measures like HIPAA compliance. Concerns about de-identified data being sold and used without explicit patient consent are valid.
- Algorithmic Bias: If AI models are trained on datasets that disproportionately represent certain demographics or contain historical biases, they can perpetuate or even amplify health inequities, leading to unequal care for different patient groups.
- Over-reliance on Technology: An excessive dependence on AI could lead to a degradation of critical thinking skills among physicians or a failure to question AI outputs, even when they seem questionable.
- Lack of Empathy and Human Connection: While AI can streamline communication, it cannot replicate genuine human empathy, compassion, or the nuanced understanding required in sensitive patient interactions. Over-automation could lead to a depersonalized healthcare experience.
- Liability Concerns: The legal and ethical responsibility for errors or adverse outcomes caused by AI remains a complex and evolving area.
- Cybersecurity Threats: AI systems themselves can be targets for cyberattacks, potentially disrupting healthcare services or compromising patient data.
How can physicians build trust in AI tools?
Building trust in AI is a multi-faceted process that requires collaboration between AI developers, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies:
- Rigorous Validation and Testing: AI tools must undergo extensive clinical validation, demonstrating their accuracy, reliability, and safety in real-world healthcare settings before widespread adoption.
- Transparent Algorithms: Whenever possible, AI models should be "explainable," allowing physicians to understand the reasoning behind the AI's recommendations. This helps build confidence and ensures appropriate clinical application.
- Continuous Education and Training: Physicians need comprehensive training on how to use AI tools effectively, understand their capabilities and limitations, and critically evaluate their outputs.
- Human Oversight and "Human-in-the-Loop" Design: AI should always function under human supervision. Systems should be designed to keep a human in the loop, ensuring that a physician reviews and validates all critical AI-generated information or decisions.
- Starting with Low-Risk Applications: Introducing AI initially for administrative tasks or as a supportive tool for diagnosis (where human review is guaranteed) can help build confidence before moving to higher-stakes applications.
- Feedback Loops: Establishing mechanisms for physicians to provide feedback on AI performance, identify errors, and suggest improvements is crucial for continuous learning and refinement of AI models.
- Strong Data Privacy Assurances: Developers must implement and clearly communicate robust data security protocols, ensuring patient data is protected and used ethically. Clear policies on data ownership and usage are vital.
- Seamless Workflow Integration: AI tools that integrate smoothly into existing EHR systems and clinical workflows are more likely to be adopted and trusted, as they reduce friction rather than create it.
By addressing these points, we can foster an environment where physicians can confidently accept AI as a valuable partner in delivering high-quality patient care.
Conclusion: Partnering with AI to Reclaim Time and Improve Care
The journey of AI for doctors is truly just beginning, yet its impact is already profound. We've seen how AI is not merely a technological novelty but a powerful force reshaping the very fabric of medical practice. From enhancing diagnostic accuracy in complex cases to revolutionizing personalized treatment plans, AI offers unprecedented opportunities to lift the standard of care.
Perhaps most critically, AI stands as a guide of hope in the fight against physician burnout. By shouldering the burden of administrative tasks—from meticulous documentation to streamlining patient communication—AI frees up doctors to do what they do best: practice medicine and connect with their patients on a human level. Imagine a world where every patient call is answered, every appointment scheduled, and every inquiry managed seamlessly, 24/7. This is the promise of purpose-built AI solutions.
The key lies in intelligent partnership. AI as an assistant, a co-pilot, a tireless data analyst—never a replacement for the invaluable human expertise and empathy that define the medical profession. The success of this integration hinges on developing and adopting custom solutions that are rigorously validated, ethically sound, and seamlessly integrated into existing workflows.
At DialIQ, we're dedicated to bringing this future to life, creating AI receptionist solutions custom for healthcare that ensure every opportunity is captured and every patient interaction is handled with efficiency and care. We believe that by embracing the right AI tools, doctors can reclaim their time, reduce stress, and ultimately dedicate more energy to the profound work of healing.
Explore AI solutions for your clinic and find how we can help you transform your practice today.


